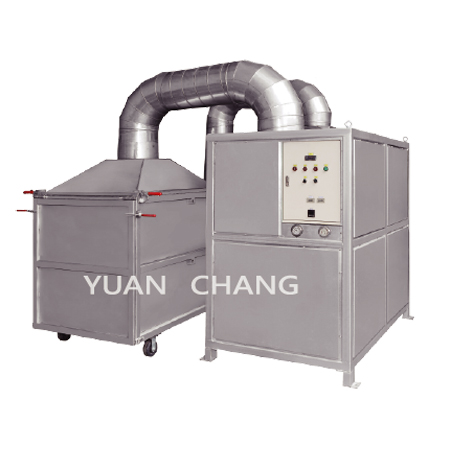
Sludge Drying Equipment
| Item No.: | CDB Series |

(Low Temperature Dehumidification Type-Batch / Continuous Treating)

Dryer is constructed by main elements including compressor, condenser, expansion valve, evaporator, auxiliary condenser and drying chamber. The expansion valve expands refrigerant into the evaporator, the refrigerant is vaporized by absorbing heat, the gaseous refrigerant compressed by the compressor to a high pressure fluid into the condenser, and release heat. The refrigerant back to the reservoir, then evaporated through the expansion valve to complete refrigeration cycle. Humidity gas withdrawn from the drying chamber through the evaporator condensate cooling and dehumidification, become dry cold. The dry cold air through the condenser air heated to a high temperature and low humidity air. High temperature and low humidity air into the drying chamber, the material water is vapored out to complete the drying cycle.
2. Purpose
- Drying process of agricultural and livestock products (please contact us).
- Drying treatment of medicine, food, chemical and other industries (please contact us).
3. Features
- Best organic sludge and inorganic sludge drying reduction system.
- Reduce sludge volume: 50%, sludge weight: over 60% and reduce disposal cost after drying.
- The power consumption of one kilogram dewatering could be 0.4~0.5 kw, you may make use of daily off-peak tariff to operate this equipment to get high economic benefit.
- Closed type, circulating, low noise, no dust, no wastewater and gas, no secondary pollution.
- Food and drug products curing for easy packing and transportation, milling and processing of agricultural products and dried herbs to improve product quality, sludge drying reduce processing costs.
- Applicable working temperature 10~40˚C.
4. Specification and Functions
High energy efficient equipment, energy consumption per kilogram of weight reduction only 0.4~0.5kw, under atmospheric pressure low temperature drying (35 ° ~ 60 ° C), treatable water content up to 75% volume reduction of 60%, the drying medium closed cycle, no emissions pollution and heat pollution.
| Model Spec. | CDB-300 | CDB-500 | CDB-1000 | CDB-1500 | CDB-2000 | CDB-3000 | CDB-5000 | |
| Treating capacity (75%→40%) L/24hr | 300 | 500 | 1000 | 1500 | 2000 | 3000 | 5000 | |
| Electricity use of dewater/kg (KWH) | 0.4 ~ 0.5 ( Inorganic ) | |||||||
| Drying temperature (℃) | 35 - 60 | |||||||
| Dry machine reference dimension (mm) | L | 1500 | 2000 | 2000 | 2400 | 2400 | 3000 | 4000 |
| W | 800 | 1100 | 1100 | 1400 | 1400 | 2000 | 2000 | |
| H | 1500 | 1750 | 1750 | 1800 | 1800 | 2000 | 2000 | |
| Dry cart / tank reference dimension (mm) | L | 1000 | 1200 | 1400 | 1200 | 1400 | 2000 | 3000 |
| W | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 2000 | 2500 | |
| H | 700 | 1000 | 1200 | 1000 | 1200 | 1200 | 1200 | |
| Number of dry cart / tank | 2 carts | 2 carts | 2 carts | 4 carts | 4 carts | 1tank | 1tank | |
| Required space (m×m) | 3×3 | 4×4 | 4×4 | 6×6 | 6×6 | 6×8 | 8×8 | |

Specification:
| Model Spec. | CD-100 | CD-250 | CD-500 | CD-750 | CD-1000 | CD-1500 | CD-2000 | CD-3000 | CD-4500 | |
| Treating capacity (85/75%→40%) | 100 | 250 | 500 | 750 | 1000 | 1500 | 2000 | 3000 | 4500 | |
| 8 hours Treating capacity (85/75%→40%) | 0.8 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 24 | 36 | |
| Max. treating capacity (85/75%→40%) | 2.4 | 6 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 36 | 48 | 72 | 108 | |
| Sludge category | Organic / Inorganic | |||||||||
| Treatable water content (%) | 85 / 75 | |||||||||
| Drying temperature (℃) | 35 ~ 60 | |||||||||
| Dry tank reference dimension (mm) | L | 2600 | 5200 | 7800 | 10400 | 13000 | 18200 | 23400 | 18200 | 18200 |
| W | 1900 | 1900 | 1900 | 1900 | 1900 | 1900 | 1900 | 1900 | 5700 | |
| H | 1990 | 1990 | 1990 | 1990 | 1990 | 1990 | 1990 | 3980 | 1990 | |
| Max. loading plate layers | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 24 | 12 | |
| Required space (m×m) | 5x4 | 7x4 | 12x4 | 13x4 | 15x4 | 20x4 | 26x4 | 20x4 | 20x10 | |
 English
English
 中文繁體
中文繁體 Русско
Русско Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Português
Português Français
Français Türk
Türk Italiano
Italiano Nederlands
Nederlands हिन्दी
हिन्दी Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia
